Halal food industry: 2019-20 'momentous' with launch of new national strategies
What were the biggest developments in the global halal food industry in 2019-2020? The State of the Global Islamic Economy 2020/21 report from DinarStandard gives a detailed breakdown of the movements in the industry, with the biggest developments being national halal strategies and the impact of COVID-19.
MARKET SIZE
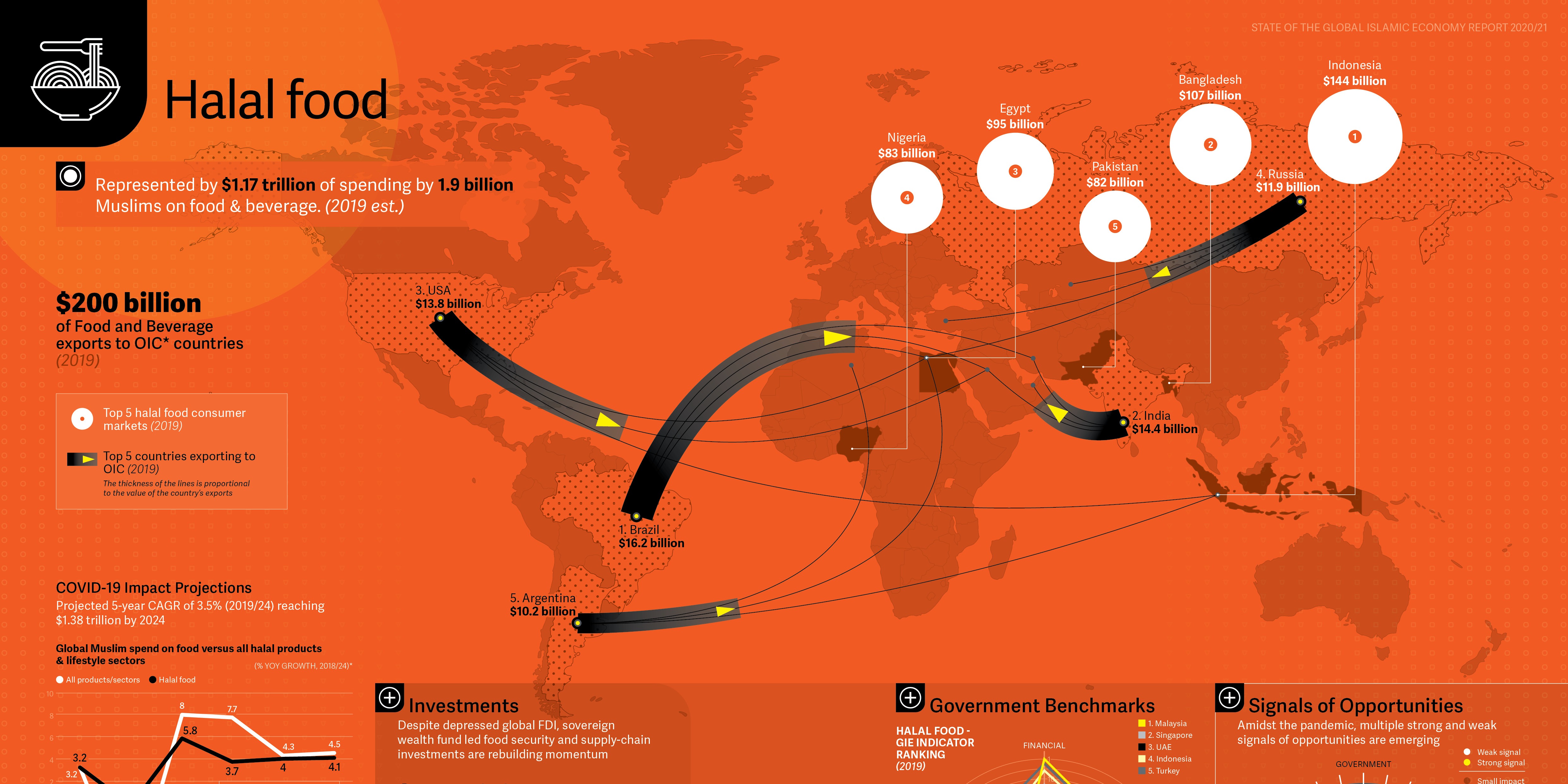
- The three biggest F&B consumer markets of the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) countries were Indonesia ($144 billion), Bangladesh ($107 billion), and Egypt ($95 billion).
- Overall, 1.9 billion Muslims around the world spent some $1.17 trillion on F&B in 2019.
- $200 billion worth of food and beverages were exported to the 57 member countries of the OIC in 2019.
- The biggest exporters were Brazil ($16.2 billion), India ($14.4 billion) and USA ($13.8 billion).
| DOWNLOAD THE STATE OF THE GLOBAL ISLAMIC ECONOMY 2020/21 REPORT |
NATIONAL HALAL STRATEGIES
2019-2020 was a "momentous period" for the halal food industry with the launch of many new national halal strategies and trade relationships, said the report.
The study from DinarStandard highlighted key developments in national halal strategies:
- Indonesia made halal certification mandatory starting October 2019 for halal food products and established the Halal Products Certification Agency (BPJPH).
-
Saudi Arabia approved the launch of the kingdom’s national system for halal products, clarifying the roles of related regulating bodies SFDA and SASO.
-
In Pakistan, the Pakistan Halal Authority (PHA) is expected to begin functioning in the federal capital to promote halal products within the country and abroad.
-
The Iranian government launched a program to integrate its halal systems to play a larger role in the halal food industry.
-
Egypt’s Council of Ministers introduced the ‘Halal in Egypt’ mark for Egyptian halal exports, while the Philippines’ Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) also launched an official national halal logo.
COVID-19 IMPACT
In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic forced import-reliant countries of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) to take immediate steps to ensure food security. Several key moves were highlighted in the report:
- Saudi Arabia pledged 2 billion riyals ($533.3 million) to fund imports and secure food via indirect and direct loan programs that will finance agricultural projects.
- The UAE government partnered with the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) to improve the country’s food safety control systems and ramp up its agriculture and aquaculture systems. It also issued a strategic food security law that ensures food supply across the country and established a public-private partnership to improve food security.
- Kuwait’s Wafra International Investment Company made a $100 million commitment to invest in Pure Harvest Smart Farms’ climate-controlled greenhouses.
PANDEMIC AND INVESTMENTS
Despite depressed global foreign direct investment due to the pandemic, sovereign wealth funds-led food security and supply chain investments are revuilding momentum.
$6.11 billion was pumped into halal-related food industry investments in 2019/2020, according to DinarStandard.
|
WHAT IS THE GROWTH AND MARKET SIZE FOR EACH SECTOR? |
© SalaamGateway.com 2020 All Rights Reserved
- The State of the Global Islamic Economy report has ben published annually since 2013.
- DinarStandard is the parent company of Salaam Gateway.